Leetcode刷题记录
3. 无重复字符的最长子串
难度中等6291
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度
解释:
- left表示无重复字符子串的最左侧位置
- right表示当前遍历到的字符的位置
- res表示最长子串的长度
- window存储每个字符的上次出现位置
- left每次更新,都需要把重复字符的上一次位置上+1,因为重复字符的上一次位置可能在开始,并不一定就比现在的left大,所以需要取二者中较大的那个。
- 每次循环都能保证当前的left是无重复子串的开始,因此每次循环都计算一遍res。
- 滑动窗口的思想是不断扩大右边界,适时缩小左边界。所以在while循环中每次都要把right的元素放进window中。
package slidingwindow;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LongestSubStringWithNoDuplicates {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) return 0;
if (s.length() == 1) return 1;
Map<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();
int left = 0, right = 0;
int res = 1;
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
while (right < chars.length) {
char cur = chars[right];
if (window.containsKey(cur)) {
left = Math.max(left, window.get(cur) + 1);
}
window.put(cur,right);
res=Math.max(res,right-left+1);
right++;
}
return res;
}
}
76. 最小覆盖子串
难度困难1679
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
注意:
- 对于
t中重复字符,我们寻找的子字符串中该字符数量必须不少于t中该字符数量。 - 如果
s中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
解释:
- tTimes表示目标字符串各个字符的统计个数
- sTimes表示目标字符串中的各个字符在s中的统计个数,在t中没有的不进行统计。
- resLen表示最终结果的字符串长度,resLeft表示最终结果字符串的起始字符的位置。resLeft+resLen表示最终结果字符串的最后一个字符的的下一个字符的位置。
- distance表示sTimes中满足tTimes中字符的总个数。
- 要注意的是sTimes只统计t中存在的字符,不统计t中不存在的字符。
- 在右指针扩大的时候要whille,在左指针缩小的时候也要用while。因为左指针缩小的过程中,可能会产生更小的符合条件的字符串。
- 在左指针缩小的过程中,要同时减少sTimes,并且,如果左边被裁掉的是t中有的字符,那么distance也应该减少。
public class MinCoverStr {
private int[] tTimes = new int[128];
private int[] sTimes = new int[128];
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
int resLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int resLeft = 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
int distance = 0;
char[] charsT = t.toCharArray();
for (char c : charsT) {
tTimes[c]++;
}
while (right < s.length()) {
char c = s.charAt(right);
if (tTimes[c] == 0) {
right++;
continue;
}
right++;
if (sTimes[c] < tTimes[c]) {
distance++;
}
sTimes[c]++;
while (distance == t.length()) {
if (right - left < resLen) {
resLen = right - left;
resLeft = left;
}
char delete = s.charAt(left);
if (tTimes[delete] != 0) {
if (tTimes[delete] == sTimes[delete]) {
distance--;
}
sTimes[delete]--;
}
left++;
}
}
return resLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(resLeft, resLeft + resLen);
}
}
567. 字符串的排列
难度中等594
给你两个字符串 s1 和 s2 ,写一个函数来判断 s2 是否包含 s1 的排列。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
换句话说,s1 的排列之一是 s2 的 子串 。
示例 1:
输入:s1 = "ab" s2 = "eidbaooo"
输出:true
解释:s2 包含 s1 的排列之一 ("ba").
示例 2:
输入:s1= "ab" s2 = "eidboaoo"
输出:false
提示:
1 <= s1.length, s2.length <= 104s1和s2仅包含小写字母
解释:
- target存放目标字符串中每个字符的个数
- window存放目标字符串中的每个字符在当前窗口的个数,不在目标字符串中的字符不进行统计。
- count统计目标字符串中不同字符的个数,也就是我们有几个字符需要满足,比方说:目标字符串为aabb,则count为2,因为只有a和b两字符,而不是4
- distance表示当前窗口有多少字符已经满足了要求
- 只有在window中某个字符的个数等于target中该字符的个数时,该字符才算满足,distance进行+1;
- 同时,在缩小左边界的时候,也只有target[charLeft] == window[charLeft]才回造成distance-1;
public class CheckInclusion {
private int[] target = new int[128];
private int[] window = new int[128];
public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
char[] chars1 = s1.toCharArray();
for (char c : chars1) {
target[c]++;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i : target) {
if (i > 0) count++;
}
int left = 0, right = 0;
int distance = 0;
while (right < s2.length()) {
char cur = s2.charAt(right);
right++;
if (target[cur] > 0) {
window[cur]++;
if (target[cur] == window[cur]) {
distance++;
}
}
while (right - left >= s1.length()) {
if (distance == count) {
return true;
}
char charLeft = s2.charAt(left);
if (target[charLeft] > 0) {
if (target[charLeft] == window[charLeft]) {
distance--;
}
window[charLeft]--;
}
left++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 076. 数组中的第 k 大的数字
难度中等7
给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。
请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class FindKthLargest {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(k,
(o1, o2) -> o1 - o2
);
for (int num : nums) {
if (queue.size() == k) {
Integer peek = queue.peek();
if (peek < num) {
queue.poll();
queue.add(num);
}
} else {
queue.add(num);
}
}
return queue.peek();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new FindKthLargest().findKthLargest(new int[]{3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4}, 2));
}
}
146. LRU 缓存机制
难度中等1638
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以正整数作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
class LRUCache {
private Integer size;
private Integer capacity;
DLinkedNode head;
DLinkedNode tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
private class DLinkedNode {
int val;
int key;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode(int key,int val) {
this.val = val;
this.key=key;
}
public DLinkedNode() {
}
}
private Map<Integer,DLinkedNode> map=new HashMap<>();
public int get(int key){
DLinkedNode node = map.get(key);
if(node==null)return -1;
moveTohead(node);
return node.val;
}
public void put(int key,int value){
DLinkedNode node = map.get(key);
if(node==null){
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key,value);
map.put(key,newNode);
addToHead(newNode);
++size;
if(size>capacity){
DLinkedNode tail = removeTail();
map.remove(tail.key);
--size;
}
}else{
moveTohead(node);
node.val=value;
}
}
private DLinkedNode removeTail() {
DLinkedNode removeTail = tail.prev;
removeNode(removeTail);
return removeTail;
}
private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev=head;
node.next=head.next;
head.next.prev=node;
head.next=node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node){
node.prev.next=node.next;
node.next.prev=node.prev;
}
private void moveTohead(DLinkedNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer> {
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
super(capacity,0.75F,true);
this.capacity=capacity;
}
public int get(int key){
return super.getOrDefault(key,-1);
}
public void put(int key,int value){
super.put(key,value);
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {
return size()>capacity;
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
912. 排序数组
难度中等384
给你一个整数数组 nums,请你将该数组升序排列。
class Solution {
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
return quickSort(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
private int[] quickSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
if(left>=right)return arr;
int partition=partition(arr,left,right);
quickSort(arr,left,partition-1);
quickSort(arr,partition+1,right);
return arr;
}
private int partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
int lo=left,hi=right;
int v=arr[left];
int i=lo,j=hi+1;
while(i<=j){
while(arr[++i]<v&&i<hi);
while(arr[--j]>v&&j>lo);
if(i>=j)break;
swap(arr,i,j);
}
swap(arr,left,j);
return j;
}
private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
206. 反转链表
难度简单1985
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode node = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next=head;
head.next=null;
return node;
}
}
25. K 个一组翻转链表
难度困难1304
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
进阶:
- 你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
- 你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
public class ReverseKGroup {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || k == 0) return head;
ListNode left = head, right = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (right == null) return head;
/*这里多保留一个节点*/
right = right.next;
}
ListNode newNode=reverse(left,right);
left.next=reverseKGroup(right,k);
return newNode;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur=left;
while(cur!=right){
ListNode next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=next;
}
return pre;
}
}
15. 三数之和
难度中等3806
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class ThreeSum {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results=new ArrayList<>();
if(nums==null||nums.length<3)return results;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int len = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(nums[i]>0)return results;
if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;
int l=i+1,r=len-1;
while(l<r){
int sum=nums[i]+ nums[l]+nums[r];
if(sum==0){
results.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[l],nums[r]));
while(l<r&&nums[l]==nums[l+1])l++;
while(l<r&&nums[r]==nums[r-1])r--;
l++;
r--;
}else if(sum<0){
l++;
}else{
r--;
}
}
}
return results;
}
}
1. 两数之和
难度简单12207
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
import java.util.*;
public class TwoSum {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int cur = nums[i];
if(map.containsKey(target-cur)){
Integer index = map.get(target - cur);
return new int[]{index,i};
}else{
map.put(target-cur,i);
}
}
return null;
}
}
141. 环形链表
难度简单1214
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
public class HasCycle {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)return false;
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head.next;
while(slow!=fast){
if(fast==null||fast.next==null)return false;
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}
53. 最大子序和
难度简单3761
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
public class MaxSubArray {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int dp[]=new int[nums.length];
dp[0]=nums[0];
int ans=dp[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i]=Math.max(dp[i-1]+nums[i],nums[i]);
ans=Math.max(ans,dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
21. 合并两个有序链表
难度简单1931
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
public class MergeTwoSortedList {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1,ListNode l2){
if(l1==null)return l2;
if(l2==null)return l1;
if(l1.val<l2.val){
l1.next=mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next=mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
难度中等1029
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class WalkNodeOfBTByLevel {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
cur.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
res.add(cur);
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int pre=nums[0];
int ans=pre;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
pre=Math.max(pre+nums[i],nums[i]);
ans=Math.max(ans,pre);
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int pre=nums[0];
int ans=pre;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
pre=Math.max(pre+nums[i],nums[i]);
ans=Math.max(ans,pre);
}
return ans;
}
}
21. 合并两个有序链表
难度简单1931
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
public class MergeTwoSortedList {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1,ListNode l2){
if(l1==null)return l2;
if(l2==null)return l1;
if(l1.val<l2.val){
l1.next=mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next=mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
难度中等1029
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class WalkNodeOfBTByLevel {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
cur.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
res.add(cur);
}
return res;
}
}
160. 相交链表
难度简单1370
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
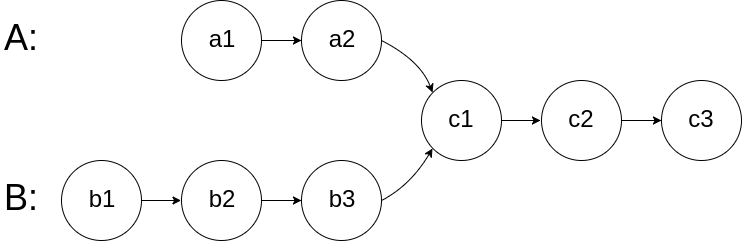
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class IntersectionNode {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (headA != null && headB != null) {
if (set.contains(headA)) return headA;
if (set.contains(headB)) return headB;
set.add(headA);
set.add(headB);
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
while (headA != null) {
headA = headA.next;
if (set.contains(headA)) return headA;
}
**while (headB != null) {
if (set.contains(headB)) return headB;
headB = headB.next;
}
**return null;
}
public ListNode getIntersectionNode1(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode point1 = headA, point2 = headB;
while (point1 != point2) {
point1 = point1 == null ? headB : point1.next;
point2 = point2 == null ? headA : point2.next;
}
return point1;
}
}
121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
难度简单1857
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int length = prices.length;
int dp[][]=new int[length][2];
dp[0][1]=-prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
dp[i][0]=Math.max(dp[i-1][0],dp[i-1][1]+prices[i]);
dp[i][1]=Math.max(dp[i-1][1],-prices[i]);
}
return dp[length-1][0];
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] nums) {
int length=nums.length;
if(length<2)return 0;
int pre0=0;
int pre1=-nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
pre0=Math.max(pre0,pre1+nums[i]);
pre1=Math.max(pre1,-nums[i]);
}
return pre0;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] nums) {
int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int res = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
minPrice = Math.min(num, minPrice);
res = Math.max(num - minPrice, res);
}
return res;
}
}
122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II
难度中等1383
给定一个数组 prices ,其中 prices[i] 是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)
public class MaxProfitWithSeveralTimes {
private int res;
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int length = prices.length;
if (length < 2) return 0;
res = 0;
dfs(prices, 0, length, 0, res);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[] prices, int index, int len, int status, int profit) {
if (index == len) {
res = Math.max(res, profit);
return;
}
dfs(prices, index + 1, len, status, profit);
if (status == 0) {
dfs(prices, index + 1, len, 1, profit - prices[index]);
} else {
dfs(prices, index + 1, len, 0, profit + prices[index]);
}
}
public int maxProfit2(int[] prices) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length - 1; i++) {
int diff = prices[i + 1] - prices[i];
if (diff > 0) {
res += diff;
}
}
return res;
}
public int maxProfit3(int[] prices) {
int len = prices.length;
if (len < 2) {
return 0;
}
// 0:持有现金
// 1:持有股票
// 状态转移:0 → 1 → 0 → 1 → 0 → 1 → 0
int[][] dp = new int[len][2];
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
// 这两行调换顺序也是可以的
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i]);
}
return dp[len - 1][0];
}
}
123. 买卖股票的最佳时机 III
难度困难877
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你最多可以完成 两笔 交易。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
public class MaxProfit3 {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int len = prices.length;
if (len < 2) return 0;
int dp[][] = new int[len][4];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][3] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 0;
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i], dp[i - 1][1]);
dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i], dp[i - 1][2]);
dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i]);
dp[i][4] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
}
return Math.max(dp[len - 1][0], Math.max(dp[len - 1][2], dp[len - 1][4]));
}
}
188. 买卖股票的最佳时机 IV
难度困难580
给定一个整数数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你最多可以完成 k 笔交易。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
public class MaxProfitWithKTimes {
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int len = prices.length;
// 特判
if (k == 0 || len < 2) {
return 0;
}
if (k >= len / 2) {
return greedy(prices, len);
}
// dp[i][j][K]:到下标为 i 的天数为止(从 0 开始),到下标为 j 的交易次数(从 0 开始)
// 状态为 K 的最大利润,K = 0 表示不持股,K = 1 表示持股
int[][][] dp = new int[len][k][2];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
dp[i][j][1]=-9999;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
if(i==0){
dp[i][j][0]=0;
dp[i][j][1]=-prices[0];
}else{
if(j==0){
dp[i][j][1]=Math.max(dp[i-1][j][1],-prices[i]);
}else{
dp[i][j][1]=Math.max(dp[i-1][j-1][0]-prices[i],dp[i-1][j][1]);
}
dp[i][j][0]=Math.max(dp[i-1][j][1]+prices[i],dp[i-1][j][0]);
}
}
}
return dp[len-1][k-1][0];
}
private int greedy(int[] prices, int len) {
// 转换为股票系列的第 2 题,使用贪心算法完成,思路是只要有利润,就交易
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
if (prices[i - 1] < prices[i]) {
res += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
}
}
return res;
}
}
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
难度中等525
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层序遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
例如:给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
import java.util.*;
public class BTZigZagWalk {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
boolean initial = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
Deque<Integer> cur = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (initial) {
cur.addLast(node.val);
} else {
cur.addFirst(node.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
initial = !initial;
res.add(new ArrayList<>(cur));
}
return res;
}
}
package tree;
import java.util.*;
public class TreeZigzagTraversal {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
boolean initial = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = q.poll();
cur.add(poll.val);
if (poll.left != null) q.add(poll.left);
if (poll.right != null) q.add(poll.right);
}
if (!initial) {
Collections.reverse(cur);
}
res.add(cur);
initial = !initial;
}
return res;
}
}
88. 合并两个有序数组
难度简单1126
给你两个按 非递减顺序 排列的整数数组 nums1 **和 nums2,另有两个整数 m 和 n ,分别表示 nums1 和 nums2 中的元素数目。
请你 合并 nums2 到 nums1 中,使合并后的数组同样按 非递减顺序** 排列。
注意:最终,合并后数组不应由函数返回,而是存储在数组 nums1 中。为了应对这种情况,nums1 的初始长度为 m + n,其中前 m 个元素表示应合并的元素,后 n 个元素为 0 ,应忽略。nums2 的长度为 n 。
public class MergeTwoSortedArrays {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int nums2[], int n) {
int index = m + n - 1;
int index1 = m - 1, index2 = n - 1;
while (index >= 0) {
if (index1 < 0) {
nums1[index--] = nums2[index2--];
continue;
}
if (index2 < 0) {
nums1[index--] = nums1[index1--];
continue;
}
if (nums1[index1] > nums2[index2]) {
nums1[index--] = nums1[index1--];
} else {
nums1[index--] = nums2[index2--];
}
}
}
}
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
难度中等1315
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class LowestCommonAncestor {
private Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> parentsMap = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
walkNodes(root);
TreeNode pParent = p;
TreeNode qParent = q;
Stack<TreeNode> pStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> qStack = new Stack<>();
pStack.push(pParent);
qStack.push(qParent);
while ((pParent = parentsMap.get(pParent)) != null) {
pStack.push(pParent);
}
while ((qParent = parentsMap.get(qParent)) != null) {
qStack.push(qParent);
}
TreeNode res = null;
while ((!pStack.isEmpty()) && (!qStack.isEmpty())) {
TreeNode pNode = pStack.pop();
TreeNode qNode = qStack.pop();
if (pNode.val== qNode.val) {
res = pNode;
} else {
return res;
}
}
return res;
}
public void walkNodes(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
parentsMap.put(node.left, node);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
parentsMap.put(node.right, node);
}
}
}
}
}
public class LowestCommonAncestorByRecursion {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left == null) return right;
if (right == null) return left;
return root;
}
}
20. 有效的括号
难度简单2672
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
import java.util.Stack;
public class ValidParentheses {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if (s.isEmpty()) return true;
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (c == '(') {
stack.push(')');
} else if (c == '{') {
stack.push('}');
} else if (c == '[') {
stack.push(']');
} else {
if (stack.isEmpty()||stack.pop()!=c) return false;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
415. 字符串相加
难度简单448
给定两个字符串形式的非负整数 num1 和num2 ,计算它们的和并同样以字符串形式返回。
你不能使用任何內建的用于处理大整数的库(比如 BigInteger), 也不能直接将输入的字符串转换为整数形式。
public class StringNumberAdd {
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
if (num1 == null || num1.isEmpty()) return num2;
if (num2 == null || num2.isEmpty()) return num1;
int len1 = num1.length();
int len2 = num2.length();
int i = len1 - 1, j = len2 - 1;
int left = 0;
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0) {
int cur1 = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i--) - '0' : 0;
int cur2 = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j--) - '0' : 0;
int temp = (cur1 + cur2 + left) % 10;
left = (cur1 + cur2 + left) / 10;
res.append(temp);
}
if (left != 0) {
res.append(left);
}
return res.reverse().toString();
}
}
5. 最长回文子串
难度中等4156
给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
public class LongestPalindrome {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.isEmpty() || s.length() == 1) return s;
int len = s.length();
String res= "";
for (int i = 0; i < len-1; i++) {
String s1 = expandFromCenter(s, i, i + 1);
String s2 = expandFromCenter(s, i, i);
if(s1.length()>s2.length()){
if(s1.length()>res.length())res=s1;
}else{
if(s2.length()>res.length())res=s2;
}
}
return res;
}
public String expandFromCenter(String s, int left, int right) {
int i = left, j = right;
while (i >= 0 && j < s.length()) {
char leftChar = s.charAt(i);
char rightChar = s.charAt(j);
if (leftChar != rightChar) break;
i--;
j++;
}
return s.substring(i + 1, j );
}
}
142. 环形链表 II
难度中等1195
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
进阶:
- 你是否可以使用
O(1)空间解决此题?
public class DetectCycle {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(true){
if(fast==null||fast.next==null)return null;
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
if(fast==slow)break;
}
ListNode pre=head;
while (pre!=slow){
pre=pre.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return pre;
}
}
public class DetectCycle {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(true){
if(fast==null||fast.next==null)return null;
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
if(fast==slow)break;
}
ListNode pre=head;
while (pre!=slow){
pre=pre.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return pre;
}
}
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
难度中等1598
整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
public class SearchRotatedSortedArray {
public int search(int nums[], int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) return mid;
if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) {
if (nums[mid] > target && nums[left] <= target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
} else {
if (nums[mid] < target && nums[right] >= target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
54. 螺旋矩阵
难度中等878
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int top = 0, bottom = m - 1, left = 0, right = n - 1;
int curX = 0, curY = 0;
while (res.size() < m * n) {
while (curY <= right) {
res.add(matrix[curX][curY]);
curY++;
}
curY--;
curX++;
if (++top > bottom) break;
while (curX <= bottom) {
res.add(matrix[curX][curY]);
curX++;
}
if (--right < left) break;
curX--;
curY--;
while (curY >= left) {
res.add(matrix[curX][curY]);
curY--;
}
if (--bottom < top) break;
curY++;
curX--;
while (curX >= top) {
res.add(matrix[curX][curY]);
curX--;
}
if (++left > right) break;
curX++;
curY++;
}
return res;
}
}
92. 反转链表 II
难度中等1041
给你单链表的头指针
head
和两个整数
left
和
right
,其中
left <= right
。请你反转从位置
left
到位置
right
的链表节点,返回
反转后的链表
。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
int len = right - left + 1;
ListNode dump = new ListNode(-1);
dump.next = head;
int leftTimes = left - 1;
ListNode preNode = dump;
while (leftTimes-- > 0) {
preNode = preNode.next;
}
ListNode rightNode = preNode;
while (len-- > 0) {
rightNode = rightNode.next;
}
ListNode leftNode = preNode.next;
preNode.next = null;
ListNode nextNode = rightNode.next;
rightNode.next = null;
helper(leftNode);
preNode.next = rightNode;
leftNode.next = nextNode;
return dump.next;
}
public ListNode helper(ListNode node) {
if (node == null || node.next == null) return node;
ListNode pre = node;
ListNode cur = node.next;
ListNode next = helper(node.next);
cur.next = pre;
pre.next = null;
return next;
}
}
46. 全排列
难度中等1577
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
class Solution {
private boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
this.used = new boolean[len];
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
backtrace(0,nums,res,len,new ArrayDeque<>());
return res;
}
private void backtrace(int index, int nums[], List<List<Integer>> res, int len, ArrayDeque<Integer> path) {
if (index == len) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (used[i]) continue;
used[i] = true;
path.addLast(nums[i]);
backtrace(index + 1, nums, res, len, path);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
704. 二分查找
难度简单440
给定一个 n 个元素有序的(升序)整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1。
public class BinarySearch {
public int search(int nums[], int target) {
int left=0,right=nums.length-1;
while (left<=right){
int mid=left+(right-left)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target)return mid;
else if(nums[mid]<target){
left=mid+1;
}else{
right=mid-1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
42. 接雨水
难度困难2743
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
public class RainTrap {
public int trap(int height[]) {
int n = height.length;
int leftMaxHeight[] = new int[n];
int rightMaxHeight[] = new int[n];
int res = 0;
leftMaxHeight[0] = height[0];
rightMaxHeight[n - 1] = height[n - 1];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
leftMaxHeight[i] = Math.max(leftMaxHeight[i - 1], height[i]);
}
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
rightMaxHeight[i] = Math.max(rightMaxHeight[i + 1], height[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
res += Math.min(leftMaxHeight[i], rightMaxHeight[i]) - height[i];
}
return res;
}
}
300. 最长递增子序列
难度中等1940
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度。
子序列是由数组派生而来的序列,删除(或不删除)数组中的元素而不改变其余元素的顺序。例如,[3,6,2,7] 是数组 [0,3,1,6,2,2,7] 的子序列。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class LongestIncrSubSequence {
public int lengthOfLIS(int nums[]) {
int length = nums.length;
int dp[] = new int[length];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
int res = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
res = Math.max(res, dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
232. 用栈实现队列
难度简单485
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
说明:
- 你只能使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有
push to top,peek/pop from top,size, 和is empty操作是合法的。 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
进阶:
- 你能否实现每个操作均摊时间复杂度为
O(1)的队列?换句话说,执行n个操作的总时间复杂度为O(n),即使其中一个操作可能花费较长时间。
import java.util.Stack;
public class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> data;
private Stack<Integer> helper;
public MyQueue() {
data = new Stack<>();
helper = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
while (!data.isEmpty()) {
helper.push(data.pop());
}
data.push(x);
while (!helper.isEmpty()) {
data.push(helper.pop());
}
}
public int pop() {
return data.pop();
}
public int peek() {
return data.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return data.isEmpty();
}
}
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
难度简单1120
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class InorderTraversal {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
helper(root);
return list;
}
private void helper(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
helper(node.left);
list.add(node.val);
helper(node.right);
}
}
143. 重排链表
难度中等682
给定一个单链表 L **的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln-1 → Ln 请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln-1 → L2 → Ln-2 → …
不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
public class ReorderList {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return;
ListNode middle = findMiddle(head);
ListNode next = middle.next;
middle.next=null;
ListNode reverse = reverse(next);
merge(head,reverse);
}
private ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null, next, cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
private void merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode temp1, temp2;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
temp1 = l1.next;
temp2 = l2.next;
l1.next = l2;
l1 = temp1;
l2.next = l1;
l2 = temp2;
}
}
}
199. 二叉树的右视图
难度中等547
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class RightViewOfTree {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
helper(root, 0);
return res;
}
public void helper(TreeNode node, int index) {
if (node == null) return;
helper(node.left, index + 1);
if (index>res.size()-1) {
res.add(node.val);
} else {
res.set(index, node.val);
}
helper(node.right, index + 1);
}
}
70. 爬楼梯
难度简单1921
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
public class ClimbStairs {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int dp[] = new int[n + 1];
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i < n + 1; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[n];
}
}
public class ClimbStairs {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
int pre= 1;
int cur = 2;
for (int i = 3; i < n + 1; i++) {
cur=pre+cur;
pre=cur-pre;
}
return cur;
}
}
public class ClimbStairs {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int dp[] = new int[n + 1];
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
int pre= 1;
int cur = 2;K
for (int i = 3; i < n + 1; i++) {
int temp=cur;
cur = cur + pre;
pre=temp;
}
return cur;
}
}
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
难度简单288
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。
例如,一个链表有 6 个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是 1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第 3 个节点是值为 4 的节点。
public class LastKthNode {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode fast = head;
while (k-- > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
难度困难1241
路径 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其 最大路径和 。
public class MaxPathSum {
private int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
getMaxPathSumOnNodeAsABranch(root);
return res;
}
public int getMaxPathSumOnNodeAsABranch(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int leftPathSum = Math.max(getMaxPathSumOnNodeAsABranch(root.left),0);
int rightPathSum = Math.max(getMaxPathSumOnNodeAsABranch(root.right),0);
int sum = leftPathSum + rightPathSum + root.val;
res = Math.max(res, sum);
return Math.max(leftPathSum,rightPathSum)+root.val;
}
}
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
难度中等1597
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n **个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
public class RemoveNthFromEnd {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dump = new ListNode(-1);
dump.next = head;
ListNode fast = dump, slow = dump;
while (n-- > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
ListNode pre = slow;
ListNode cur = slow.next;
ListNode next = slow.next.next;
pre.next = next;
cur.next = null;
return dump.next;
}
}
2. 两数相加
难度中等6860
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
public class AddTwoNumberInNode {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int left = 0;
ListNode dump = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dump;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
int val1 = l1.val;
int val2 = l2.val;
int sum = (val1 + val2 + left);
int res = sum % 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(res);
left = sum / 10;
l1=l1.next;
l2=l2.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
while(l1!=null){
int val1 = l1.val;
int sum = (val1 + left);
int res = sum % 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(res);
left = sum / 10;
l1=l1.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
while (l2!=null){
int val2 = l2.val;
int sum = (val2 + left);
int res = sum % 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(res);
left = sum / 10;
l2=l2.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
if(left!=0){
cur.next = new ListNode(left);
}
return dump.next;
}
}
public class AddTwoNumberInNode {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int left = 0;
ListNode dump = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dump;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null || left != 0) {
int val1 = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int val2 = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int sum = (val1 + val2 + left);
int res = sum % 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(res);
left = sum / 10;
if (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dump.next;
}
}
56. 合并区间
难度中等1126
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeIntervals {
public int[][] mergeIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
Arrays.sort(intervals, (o1, o2) ->
o1[0] == o2[0] ? o1[1] - o2[1] : o1[0] - o2[0]
);
int i=0,j=0;
while (++j<intervals.length){
if(intervals[i][1]>=intervals[j][0]){
intervals[i][1]=Math.max(intervals[i][1],intervals[j][1]);
}else{
intervals[++i]=intervals[j];
}
}
return Arrays.copyOf(intervals,i+1);
}
}
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
难度简单660
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 **遍历。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TreePreOrder {
private List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
helper(root);
return res;
}
public void helper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
res.add(root.val);
helper(root.left);
helper(root.right);
}
}
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
难度中等727
存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点 head ,请你删除链表中所有存在数字重复情况的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 **的数字。
返回同样按升序排列的结果链表
public class DeleteDuplicatesInList {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode needle = new ListNode(-1);
needle.next = head;
ListNode res = needle;
while (needle.next != null) {
int val = needle.next.val;
if (needle.next.next != null && needle.next.next.val == val) {
ListNode nextTarget = needle.next.next;
while (nextTarget != null && nextTarget.val == val) {
nextTarget = nextTarget.next;
}
needle.next = nextTarget;
} else {
needle = needle.next;
}
}
return res.next;
}
}
public class DeleteDuplicatesInList {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode next = head.next;
if (next.val == head.val) {
while (next != null && next.val == head.val) {
next = next.next;
}
head = deleteDuplicates(next);
} else {
head.next = deleteDuplicates(next);
}
return head;
}
}
148. 排序链表
难度中等1322
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
进阶:
- 你可以在
O(n log n)时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
public class SortList {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode middleNode = findMiddleNode(head);
ListNode middleNextNode = middleNode.next;
middleNode.next=null;
ListNode leftNode = sortList(middleNode);
ListNode rightNode = sortList(middleNextNode);
return merge(leftNode, rightNode);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null)return l2;
if(l2==null)return l1;
if(l1.val<l2.val){
l1.next=merge(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next=merge(l2.next,l1);
return l2;
}
}
private ListNode findMiddleNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
public class SortList {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode middleNode = findMiddleNode(head);
ListNode middleNextNode = middleNode.next;
middleNode.next=null;
ListNode leftNode = sortList(head);
ListNode rightNode = sortList(middleNextNode);
return merge(leftNode, rightNode);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dump=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur=dump;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
cur.next=l1;
l1=l1.next;
}else{
cur.next=l2;
l2=l2.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=l1!=null?l1:l2;
return dump.next;
}
private ListNode findMiddleNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
31. 下一个排列
难度中等1361
实现获取 下一个排列 的函数,算法需要将给定数字序列重新排列成字典序中下一个更大的排列(即,组合出下一个更大的整数)。
如果不存在下一个更大的排列,则将数字重新排列成最小的排列(即升序排列)。
必须 原地 修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class NextPermutation {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
int reverseStart = len - 1, beforeReverseStart = len - 2;
while (beforeReverseStart >= 0) {
if (nums[beforeReverseStart] < nums[reverseStart]) {
break;
} else {
reverseStart--;
beforeReverseStart--;
}
}
int needToSwap = len - 1;
while (needToSwap >= beforeReverseStart && beforeReverseStart >= 0) {
if (nums[needToSwap] > nums[beforeReverseStart]) {
swap(nums, needToSwap, beforeReverseStart);
break;
} else {
needToSwap--;
}
}
Arrays.sort(nums, reverseStart, len);
}
private void swap(int nums[], int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
76. 最小覆盖子串
难度困难1375
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
注意:
- 对于
t中重复字符,我们寻找的子字符串中该字符数量必须不少于t中该字符数量。 - 如果
s中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
public class MinWindowToCoverTargetCharacters {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
int sLen = s.length();
int tLen = t.length();
int sTimes[] = new int[128];
int tTimes[] = new int[128];
for (int i = 0; i < tLen; i++) {
char c = t.charAt(i);
tTimes[c]++;
}
int left = 0, right = 0, count = 0;
int resLeft = 0, resLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (right < sLen) {
char c = s.charAt(right);
if (tTimes[c] == 0) {
right++;
continue;
}
right++;
if (sTimes[c] < tTimes[c]) {
count++;
}
sTimes[c]++;
while (count == tLen) {
if (right - left < resLen) {
resLeft = left;
resLen = right - left;
}
char delete = s.charAt(left);
if (tTimes[delete] != 0) {
if (tTimes[delete] == sTimes[delete]) {
count--;
}
sTimes[delete]--;
}
left++;
}
}
return resLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(resLeft, resLeft + resLen);
}
}
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
难度中等1253
给定一棵树的前序遍历 preorder 与中序遍历 inorder。请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class BuildTreeWithPreAndInOrder {
private int[] preorder;
private int[] inorder;
private int preIndex = 0;
private Map<Integer, Integer> positions = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
this.inorder = inorder;
this.preorder = preorder;
for (int i = 0; i < preorder.length; i++) {
positions.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return helper(0, inorder.length);
}
public TreeNode helper(int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) return null;
int val = preorder[preIndex];
Integer mid = positions.get(val);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(val);
preIndex++;
root.left = helper(left, mid);
root.right = helper(mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
难度中等432
给你一个二叉树的根节点
root
,树中每个节点都存放有一个
0
到
9
之间的数字。
每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
- 例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径
1 -> 2 -> 3表示数字123。
计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
叶节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
public class SumNodeValFromRootToLeaves {
/*类比于求路径总和*/
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
return helper(root, 0);
}
private int helper(TreeNode root, int path) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int temp = path * 10 + root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return temp;
}
return helper(root.left, temp) + helper(root.right, temp);
}
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度
难度简单993
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
public class MaxDepthOfBT {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
113. 路径总和 II
难度中等600
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
package array;
import tree.TreeNode;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class PathSumEqualToTarget {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int target;
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {
helper(root, new ArrayDeque<Integer>(), 0);
return res;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, ArrayDeque<Integer> path, int cur) {
if (root == null) return;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (cur == target) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
//这个地方不能return,因为path还没有removeLast呢
//每一个分支的path都只有一个,必须及时清理path的最后一个。
//这一点和递归不同。
}
}
cur += root.val;
path.addLast(root.val);
helper(root.left, path, cur);
helper(root.right, path, cur);
path.removeLast();
}
}
72. 编辑距离
难度困难1859
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 **所使用的最少操作数 。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
- 插入一个字符
- 删除一个字符
- 替换一个字符
class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int len1 = word1.length();
int len2 = word2.length();
int dp[][] = new int[len1 + 1][len2 + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= len1; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= len2; i++) {
dp[0][i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= len1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= len2; j++) {
if (word1.charAt(i-1) == word2.charAt( j- 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1, dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
private int min(int a, int b, int c) {
return Math.min(a, Math.min(b, c));
}
}
41. 缺失的第一个正数
难度困难1228
给你一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,请你找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数。
请你实现时间复杂度为
O(n)
并且只使用常数级别额外空间的解决方案。
public class FindFirstMissingSmallestPositive {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= nums.length && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1]) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[temp - 1];
nums[temp - 1] = temp;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i + 1) return i + 1;
}
return nums.length + 1;
}
}
1143. 最长公共子序列
难度中等717
给定两个字符串 text1 和 text2,返回这两个字符串的最长 公共子序列 的长度。如果不存在 公共子序列 ,返回 0 。
一个字符串的 子序列 **是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
- 例如,
"ace"是"abcde"的子序列,但"aec"不是"abcde"的子序列。
两个字符串的 公共子序列 是这两个字符串所共同拥有的子序列。
public class LongestCommonSequence {
public int longestCommonSequence(String text1, String text2) {
int len1 = text1.length();
int len2 = text2.length();
int dp[][] = new int[len1 + 1][len2 + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= len1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= len2; j++) {
if (text1.charAt(i) == text2.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
}